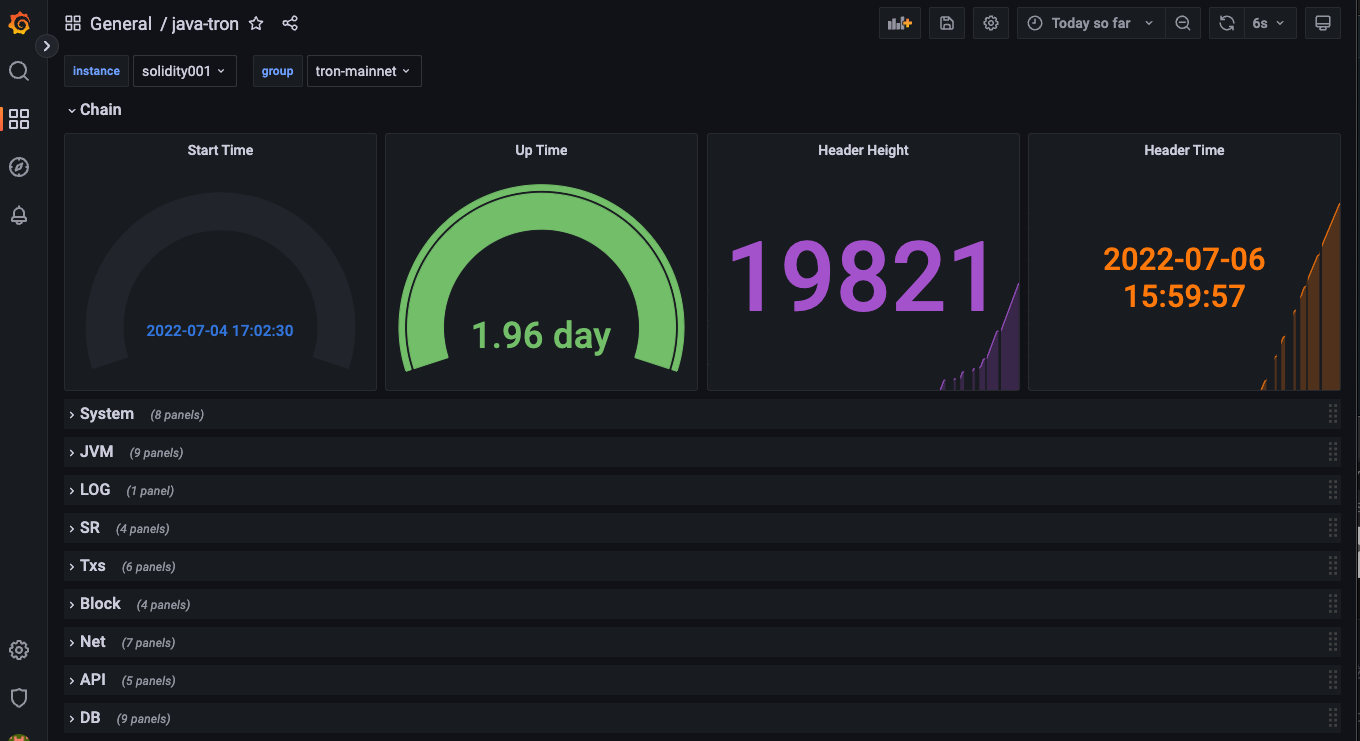
Java-tron Node Metrics Monitoring¶
Starting from the GreatVoyage-4.5.1 (Tertullian) version, the node provides a series of interfaces compatible with the prometheus protocol, so that the node deployer can monitor the health status of the node more conveniently. If you want to monitor various indicators of the node, you first need to deploy a prometheus service to communicate with the java-tron node, and obtain the indicator data of the node through the node interface. Then you need to deploy a visualization tool, such as Grafana, to display the node data obtained by prometheus in the form of a graphical interface. The following will introduce the deployment process of the java-tron node monitoring system in detail.
Configure Java-tron¶
To use the Prometheus tool to monitor the java-tron node, you first need to enable prometheus metric monitoring in the node configuration file and set the http port:
node {
... ...
p2p {
version = 11111 # 11111: mainnet; 20180622: testnet
}
####### add for prometheus start.
metrics{
prometheus{
enable=true
port="9527"
}
}
####### add for prometheus end.
}
Start Java-tron node¶
Start Java-tron node using below command:
$ java -Xmx24g -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -jar FullNode.jar -c main_net_config.conf
Deploy prometheus service¶
prometheus officially provides precompiled binaries and docker images, you can download them directly from the official website or pull the docker images on dockerhub. For more detailed installation and configuration instructions, Please refer to the prometheus documentation. As a simple deployment instruction, this article will adopt the docker image deployment:
-
After installing docker, enter the following command to pull the prometheus image:
$ docker pull prom/prometheus -
Download the prometheus configuration file
The following is a prometheus configuration file template
prometheus.yaml:You can download and use this template and modify the configuration itemsglobal: scrape_interval: 30s scrape_timeout: 10s evaluation_interval: 30s scrape_configs: - job_name: java-tron honor_timestamps: true scrape_interval: 3s scrape_timeout: 2s metrics_path: /metrics scheme: http follow_redirects: true static_configs: - targets: - 127.0.0.1:9527 labels: group: group-xxx instance: xxx-01 - targets: - 172.0.0.2:9527 labels: group: group-xxx instance: xxx-02targets, it is used to configure the ip and prometheus port of the java-tron node. If you deploy multiple java-tron nodes, you can configure multipletargetsto monitor multiple nodes. -
Start a Prometheus container
Start a Prometheus container with the following command and specify to use the user-defined configuration file in the previous step:
/Users/test/deploy/prometheus/prometheus.yaml$ docker run --name prometheus \ -d -p :9090:9090 \ -v /Users/test/deploy/prometheus/prometheus.yaml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \ prom/prometheus:latestAfter the container starts, you can view the running status of the prometheus service through
http://localhost:9090/.Click "Status" -> "Configuration" to check whether the configuration file used by the container is correct:

Click "Status" -> "Targets" to view the status of each monitored java-tron node:
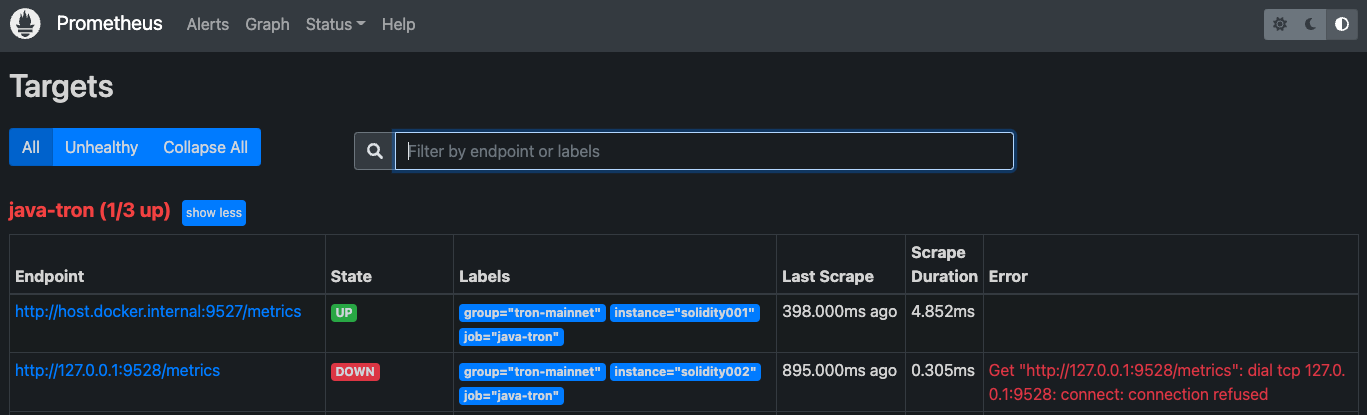
In this example, the status of the first endpoint is
UP, which means that Prometheus can fetch the data of this node normally. The second endpoint, whose status isDOWN, indicates an exception. For details, please refer to the description in "Error".When the status of the monitored java-tron nodes is normal, you can monitor the indicator data through visualization tools such as Grafana or Promdash, etc. This article will use grafana to display the data:
Deploy Grafana¶
The deployment process of the Grafana visualization tool is as follows:
-
Install Grafana Please refer to the official documentation to install Grafana. This article will adopt the docker image deployment, and the pulled image version is the open source version:
$ docker pull grafana/grafana-oss -
Start Grafana
You can use the below command to start Grafana:
$ docker run -d --name=grafana -p 3000:3000 grafana/grafana-oss -
Log in to the Grafana web UI
After startup, you can login the Grafana web UI through
http://localhost:3000/. The initial user name and password are bothadmin. After login, change the password according to the prompts, and then you can enter the main interface. Click the settings icon on the left side of the main page and select "Data Sources" to configure Grafana's data sources:
Enter the ip and port of the prometheus service in
URL: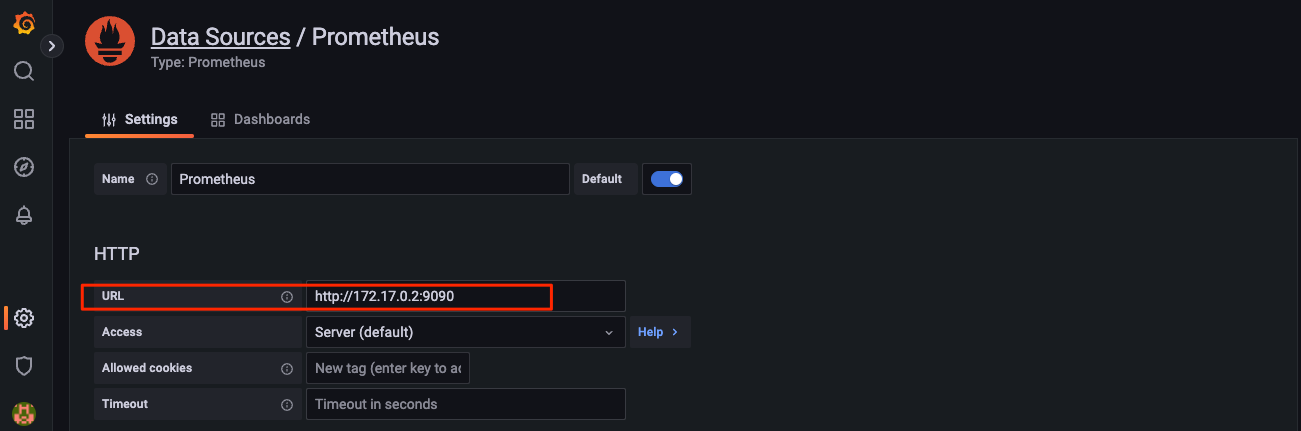
Then click the "Save & test" button at the bottom of the page to save the settings. After clicking save, Grafana will detect the connection with the data source, and if the connection is successful, you will find the words
Data source is working. -
Import Dashboard
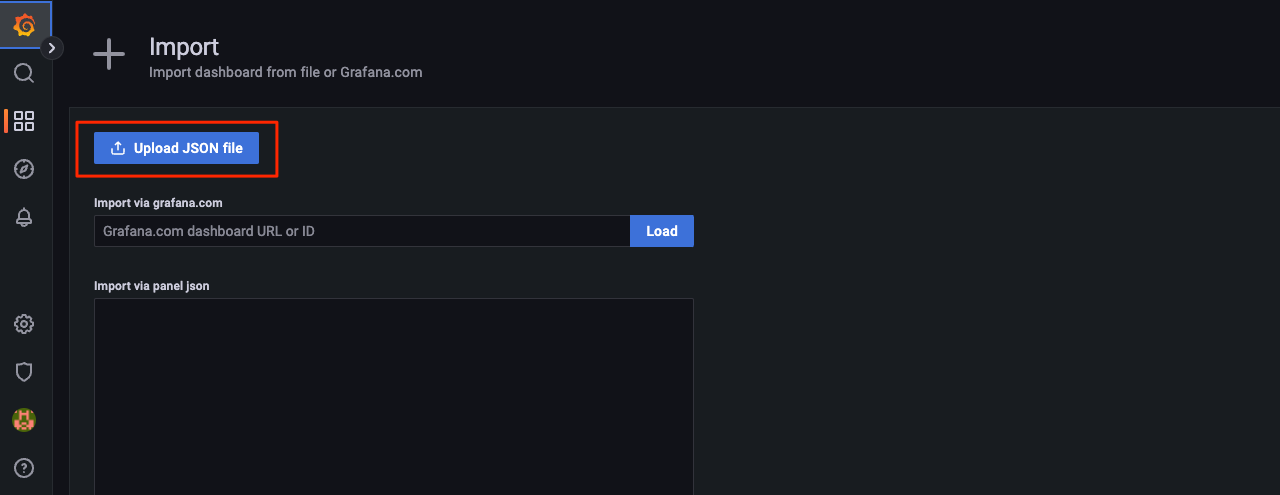
Grafana's dashboard needs to be configured. For the convenience of java-tron node deployers, the TRON community provides a comprehensive dashboard configuration file java-tron-template_rev1.json, which you can download directly and then import into Grafana.
Click the Dashboards icon on the left, then select "+Import", then click "Upload JSON file" to import the downloaded dashboard configuration file:
Then you can see the following types of monitoring metrics on the dashboard, and monitor the running status of the nodes in real time: